반응형
Using "if" in Python
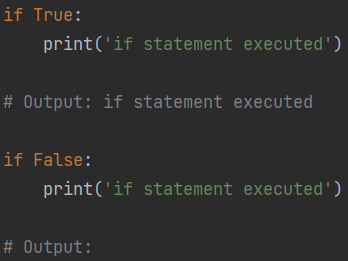
Table of Contents
* Code is basically composed of <input # output> format.
Basic Form (1): if
if condition:
statement- If the condition is True (or 1), the statement is executed.
- If the condition is False (or 0), the statement is not executed.
if True:
print('if statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if False:
print('if statement executed')
# Output:
Basic Form (2): if else
if condition:
statement
else:
statement- If the condition is True (or 1), the statement in the "if" block is executed.
- If the condition is False (or 0), the statement in the "else" block is executed.
if 1:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if 0:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
Basic Form (3): if elif else
if condition:
statement
elif condition:
statement
...
elif condition:
statement
else:
statement- If a condition in "if" or "elif" is True (or 1), the corresponding statement is executed.
- If all conditions are False (or 0), the statement in the "else" block is executed.
- Starting from the top, only the first "if" or "elif" block with a True (or 1) condition is executed.
a = 0
if a == 0:
print('if statement executed')
elif a == 1:
print('elif statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
a = 1
if a == 0:
print('if statement executed')
elif a == 1:
print('elif statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: elif statement executed
a = 2
if a == 0:
print('if statement executed')
elif a == 1:
print('elif statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
a = 3
if a == 0:
print('if statement executed')
elif a == 1:
print('first elif statement executed')
elif a == 2:
print('second elif statement executed')
elif a == 3:
print('third elif statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: third elif statement executed
Types of Conditions: Existence of Elements in an Object
- Here, an object typically refers to a string, list, tuple, or dictionary.
- If there is at least one element in the object, it evaluates to True.
- If there are no elements, it evaluates to False.
if 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if '':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
if [1, 2, 3]:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if []:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
Types of Conditions: in, not in
- Here, an object typically refers to a string, list, tuple, or dictionary.
- element in object: Evaluates to True if the specific element exists within the object, otherwise evaluates to False.
- element not in object: Evaluates to True if the specific element does not exist within the object, otherwise evaluates to False.
if 'a' in 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if 'k' in 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
if 6 not in [1, 2, 3]:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if 1 not in [1, 2, 3]:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
Types of Conditions: Comparison Operators (==, !=, >, >=, <, <=)
- Here, values typically refer to numbers or strings.
- value1 == value2: True if the two values are equal, False if they are not.
- value1 != value2: True if the two values are different, False if they are the same.
- value1 > value2: True if value1 is greater than value2, False if it is less than or equal to value2.
- value1 >= value2: True if value1 is greater than or equal to value2, False if it is less than value2.
- value1 < value2: True if value1 is less than value2, False if it is greater than or equal to value2.
- value1 <= value2: True if value1 is less than or equal to value2, False if it is greater than value2.
- object1 is object2: True if object1 and object2 are the same, False if they are different.
- object1 is not object2: True if object1 and object2 are different, False if they are the same.
- Value Comparison: == and != check if two values are equal or not (e.g., do the characters match? Is the numerical value the same?). These operators are recommended for simple value comparisons.
- Object Comparison: is and is not check if the objects themselves are the same, considering data type, memory address, etc. These operators are generally used for equality comparison of objects created through classes.
- Example: 3 == 3.0 returns True because the values are equal, but 3 is 3.0 returns False because the data type and memory address are different.
if 'abc' == 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if 'abc' != 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
if 3 >= 2:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if 3 < 2:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
if 3 is 3.0:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
Types of Conditions: Logical Operators (and, or, not)
- condition1 and condition2: True if both condition1 and condition2 are True, otherwise False.
- condition1 or condition2: True if either condition1 or condition2 is True, otherwise False.
- not condition: True if the condition is False, False if the condition is True.
- and and or can be used to connect multiple conditions.
- Example: condition1 and condition2 or condition3 and condition4 or condition5 and condition6 ...
if 1 == 1 and 'kkk' not in 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if 5 == 1 and 'kkk' not in 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: else statement executed
if 5 == 1 or 'kkk' not in 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if not 5 == 1:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
if 1 == 1 and 2 == 2 and 3 == 3:
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
Conditional Expression in if Statement
(statement if True) if (condition) else (statement if False)if 'a' in 'abc':
print('if statement executed')
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
print('if statement executed') if 'a' in 'abc' else print('else statement executed')
# Output: if statement executed
To Leave the Statement Empty: pass
- When pass is used in place of a statement, nothing happens even if the condition is met.
if 1 == 1:
pass
else:
print('else statement executed')
# Output:
반응형
'개발 > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] Comprehensive Guide to Using "for" Loops (0) | 2024.07.24 |
|---|---|
| [파이썬, Python] pdb 활용법 총정리 (1) | 2024.07.17 |
| [파이썬, Python] assert 활용법 총정리 (0) | 2024.07.17 |
| [파이썬, Python] 제너레이터 활용법 총정리 (0) | 2024.07.15 |
| [파이썬, Python] 디버깅 예시 총정리 (3) | 2024.07.15 |
